Enclosures of the Mind: Intellectual Monopolies
Enviado por ETC Staff el
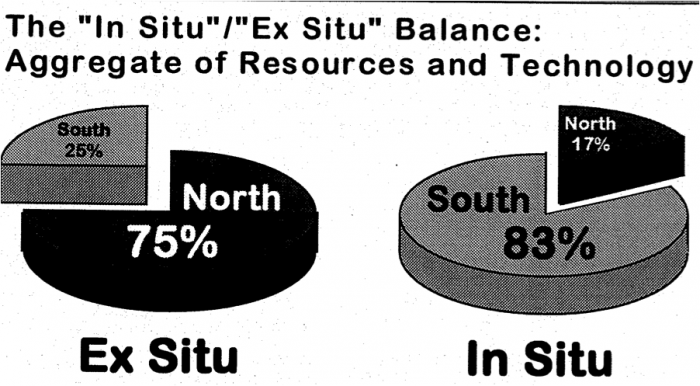
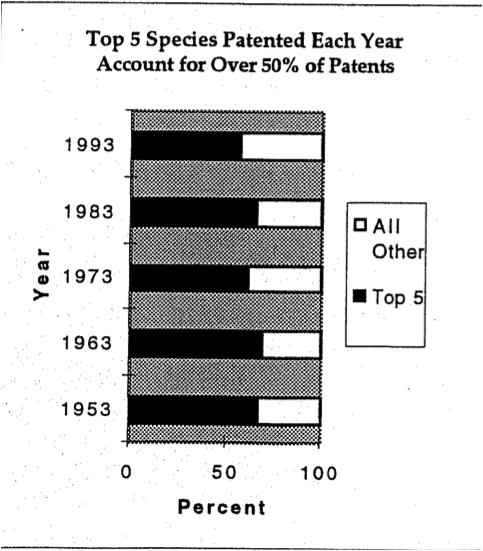
An introduction to intellectual property monopolies. The 70 page booklet produced by IDRC in 1996 is designed as an information and advocacy tool for civil society and policymakers in response to two new, legally binding international agreements: the Convention on Biological Diversity and the World Trade Organization's Trade Related Intellectual Property Agreement (WTO/TRIPs).